Working together to detect maliciously
or mistakenly issued SM2 SSL certificates.
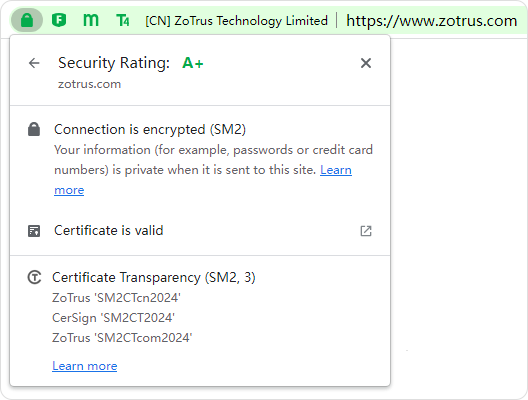
SM2CT, an ecosystem that makes the issuance of SM2 SSL certificates transparent and verifiable.

Certificate Transparency is an RFC standard (RFC 6962, RFC 9162), which is intended to detect in real time that CA system has been hacked and maliciously issued SSL certificate or that CA operator mistakenly issued SSL certificates that are not voluntarily applied by users and allow browsers to block illegal issued SSL certificate in time, to protect the security of https encryption.
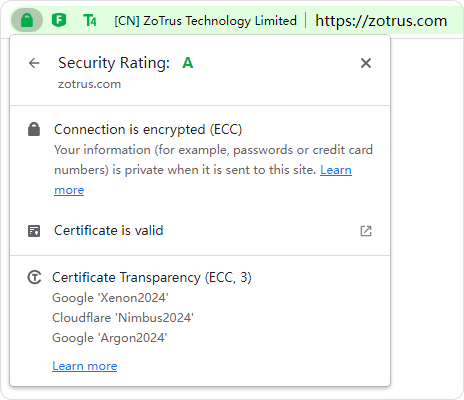
The certificate transparency log system initiated by Google has recorded 7.4 billion SSL certificates since 2013, and it is increasing at a rate of at least 100 million per month. Since Google Chrome version 68 (May 2018), it has been mandatory that every SSL certificate issued by all CAs in the world must be submitted to the specified Certificate Transparency log, then it will be trusted by browsers, effectively protects the security of the SSL certificate itself.
With Certificate Transparency logs, website owners, browsers, academics, and other interested parties can analyze and monitor logs. They were able to see which CAs issued SSL certificates when and for which domains.
CT Logs use a special cryptographic mechanism, a Merkle tree, to allow public audits. Logs are:
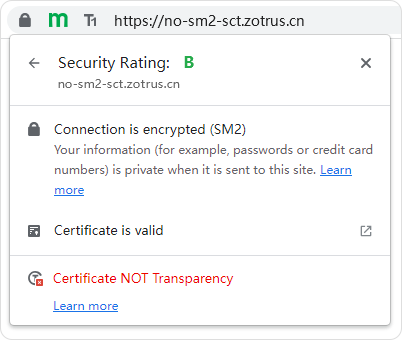
Currently, the Certificate Transparency log system (referred to as: International Certificate Transparency or ICT) led by Google only logs the SSL certificates using RSA or ECC algorithm, and it does not support the SM2 SSL certificate that cannot be used to ensure the security of SM2 SSL certificate.
The SM2 Certificate Transparency log system is developed, operated, and maintained by ZoTrus Technology based zero trust principals. It refers to the RFC 9162 international standard, which provides one more layer of security protection for SM2 SSL certificate, and also provides one more layer of security protection for the website that deploys the SM2 SSL certificate.
At present, ZT Browser has included three certificate transparency log service operated and maintained by ZoTrus Technology. All SM2 SSL certificates issued by CerSign Technology and ZoTrus Technology have been logged in these three log servers.

All can join the SM2 Certificate Transparency Program, and jointly contribute to the security of SM2 SSL Certificate, especially the security of the website using the SM2 SSL Certificate.
This is the world's first certificate transparency log system implemented with the SM2 algorithm and is the first to provide certificate transparency log service for the SM2 SSL certificates issued by CerSign Technology and ZoTrus Technology that it enhances the confidence and trust to the SM2 SSL certificates issued by CerSign and ZoTrus. Welcome other CAs that issue SM2 SSL certificates to use the ZoTrus SM2 Certificate Transparent Log Service to provide transparent protection for the SM2 SSL certificates they issued.
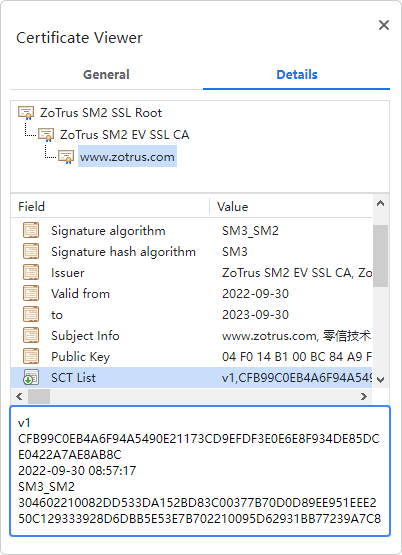
ZoTrus SM2 Certificate Transparency Log Service only accepts SM2 algorithm SSL certificates, and it is temporarily limited to the SM2 SSL certificates issued by the root CA trusted by ZT Browser.
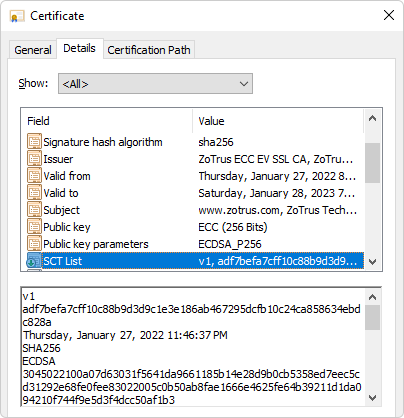
There are three ZoTrus SM2 Certificate Transparency Log Services: https://log.sm2ct.cn, https://sm2ct.cersign.cn and https://log.sm2ct.com, located at JD Cloud Guangzhou node, Tencent Cloud Guangzhou node, and China Telecom TianyiCloud Guizhou node. Currently, ZT Browser requires that SM2 SSL certificates must contain two SCT data from these three logs. More SCT data will be required depending on the situation when more SM2 certificate transparency log systems are available.
In addition to providing the SM2 certificate transparency log service for CA roots trusted by ZT Browser, ZoTrus SM2 Certificate Transparency Log System will also automatically accept the SM2 SSL certificates that are automatically collected by ZT Browser and not submitted to ZoTrus SM2 Certificate Transparency Log System, this is for all Internet users inquiring the unlogged SM2 SSL certificates.
Learn more